Dawn of nano-robot: micro-doctor in blood
In science fiction movies, we have imagined countless times that tiny robot fleets cruise in blood vessels, repair damaged tissues and remove viruses. This used to be pure imagination, but now, with the rapid development of nano-robotics, this vision is moving from science fiction to science. These micro-machines as small as nanometer scale (one billionth of a meter) are quietly starting a medical revolution.
Imagine a robot that is only a few hundred nanometers in size, smaller than blood cells, and can freely shuttle through your blood. This is not a distant concept. Researchers are designing and manufacturing different types of nano-robots, some of which can be controlled by external magnetic fields, some can respond to chemical signals in the body, and some can even be driven by biofuels. The design inspiration of these micro-robots often comes from nature, such as some "swimmers" who can use flagella to move like bacteria, or "adherents" who can attach to cells like viruses. This bionic design enables the nano-robot to better adapt to the complex biological environment and realize more precise movement and control.
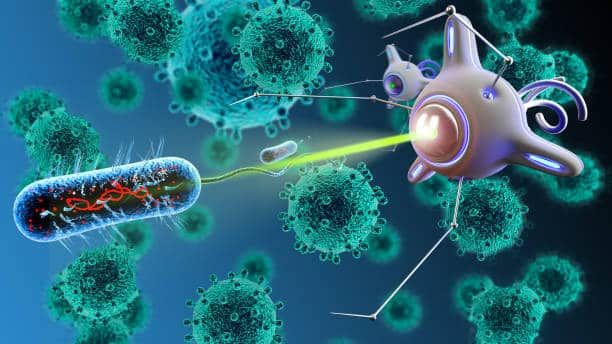
The most striking application field of nano-robots is undoubtedly (targeted drug delivery). Traditional chemotherapy drugs will indiscriminately attack all rapidly dividing cells, whether cancer cells, healthy hair follicle cells or immune cells, which leads to serious side effects. Nano-robots can be programmed to only recognize and attach to the surface of cancer cells, and then release drugs accurately. It's like putting GPS on drugs to ensure that they only reach where they are needed, thus greatly improving the treatment effect and reducing the damage to healthy tissues.
In addition to drug delivery, nano-robots have broader application prospects. In terms of diagnosis, they can be used as "scouts in the body", looking for biomarkers of early cancer in the blood, or detecting precursors of cardiovascular diseases. They can monitor blood sugar level in real time and provide more accurate insulin dosage for diabetic patients. In tissue repair, nano-robots can transport growth factors, guide stem cell differentiation, accelerate wound healing or repair damaged nerves. Scientists are even exploring how to make nano-robots remove atherosclerotic plaques and fundamentally solve the problem of heart disease.
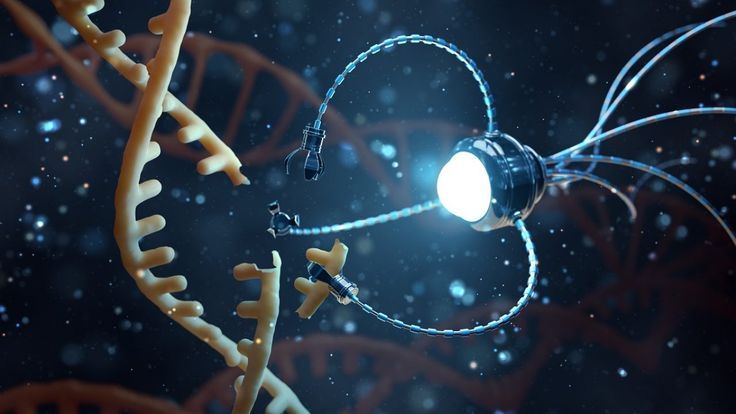
Of course, it is not easy to turn science fiction into reality. The manufacturing process of nano-robot is extremely complicated, and its safety and biocompatibility in vivo are the main challenges at present. How to ensure that they can be safely excreted after completing the task and how to avoid the attack of the immune system are the key problems to be solved. Scientists are studying degradable materials and biocompatible coatings in order to solve these bottlenecks.
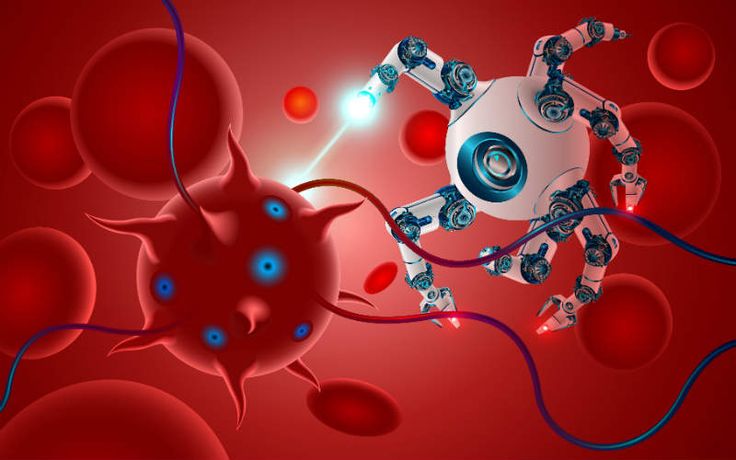
Despite the challenges, the potential of nano-robots is enormous. They are not only tools, but also a brand-new treatment concept-through intervention at the cellular and molecular levels, medicine will be upgraded from macroscopic "external repair" to microscopic "internal management". With the progress of materials science, microelectronics technology and bioengineering, we have reason to believe that in the near future, these tiny "doctors in the blood" will become our most powerful allies in fighting diseases.
(Writer:Tick)





